Western Arizona (WACOG) vs. Arizona Comparative Trends Analysis: Total Employment Growth and Change, 1969-2022 Introduction  Western Arizona (WACOG): 2022 Jobs = 185,658 2022 Percent of State = 4.33% Arizona: 2022 Jobs = 4,287,595 2022 Percent of U.S. = 2.02% Employment numbers remain the most popular and frequently cited statistics used for tracking local area economic conditions and trends. The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) employment estimates reported measure the number of full- and part-time wage and salary employees, plus the number of proprietors of unincorporated businesses. People holding more than one job are counted in the employment estimates for each job they hold. This means BEA employment estimates represent a job count, not a people count. Also, BEA employment is by place-of-work, rather than by place-of-residence. Jobs held by neighboring county residents who commute to Western Arizona (WACOG) to work are included in the employment count for Western Arizona (WACOG). Data Definition: The BEA employment series for states and local areas comprises estimates of the number of jobs, full-time plus part-time, by place of work. Full-time and part-time jobs are counted at equal weight. Employees, sole proprietors, and active partners are included, but unpaid family workers and volunteers are not included. Proprietors employment consists of the number of sole proprietorships and the number of partners in partnerships. The description "by place of work" applies to the wage and salary portion of the series and, with relatively little error, to the entire series. The proprietors employment portion of the series, however, is more nearly by place of residence because, for nonfarm sole proprietorships, the estimates are based on IRS tax data that reflect the address from which the proprietor's individual tax return is filed, which is usually the proprietor's residence. The nonfarm partnership portion of the proprietors employment series reflects the tax-filing address of the partnership, which may be either the residence of one of the partners or the business address of the partnership. The employment estimates are designed to be consistent with the estimates of wages and salaries and proprietors' income that are part of the personal income series. The employment estimates are based on the same sets of source data as the corresponding earnings estimates and are prepared with parallel methodologies. Two forms of proprietors' income-the income of limited partnerships and the income of tax-exempt cooperatives-have no corresponding employment estimates. Total Employment, 1983-2022 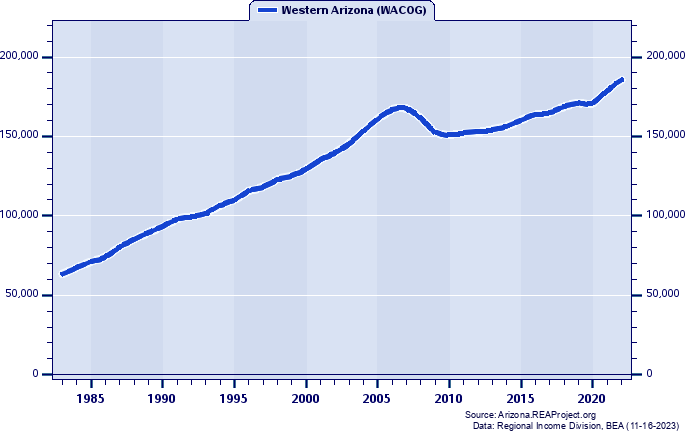 Figure 1. Figure 1 tracks Western Arizona (WACOG)'s annual total employment for the period 1983-2022 to illustrate total employment patterns over time. During this 40-year period, Western Arizona (WACOG)'s total employment rose from 63,347 in 1983 to 185,658 in 2022, for a net gain of 122,311, or 193.08%. Total Employment, 1969-2022 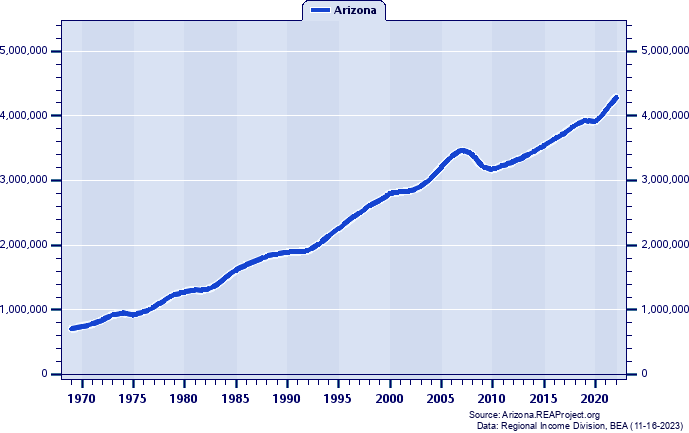 Figure 2. Figure 2 tracks Arizona's annual total employment for the period 1969-2022 to illustrate total employment patterns over time. During this 54-year period, Arizona's total employment rose from 711,344 in 1969 to 4,287,595 in 2022, for a net gain of 3,576,251, or 502.75%. Total Employment Indices (1983=100): 1983-2022 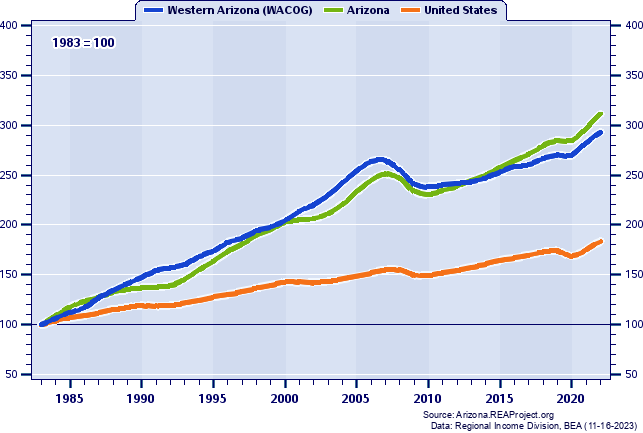 Figure 3. Figure 3 portrays Western Arizona (WACOG)'s total employment growth in a broader context by offering direct comparisons across time with Arizona, the United States. The growth indices shown here express each region's total employment in 1983 as a base figure of 100, and the total employments in later years as a percentage of the 1983 base figure. This method allows for more direct comparison of differences in total employment growth between regions that may differ vastly in size. Western Arizona (WACOG)'s overall total employment growth was 193.08% over 1983-2022 trailed Arizona's increase of 211.01%, and outpaced the United States' increase of 83.70%. Total Employment as a Percent of the Arizona Total: 1983-2022 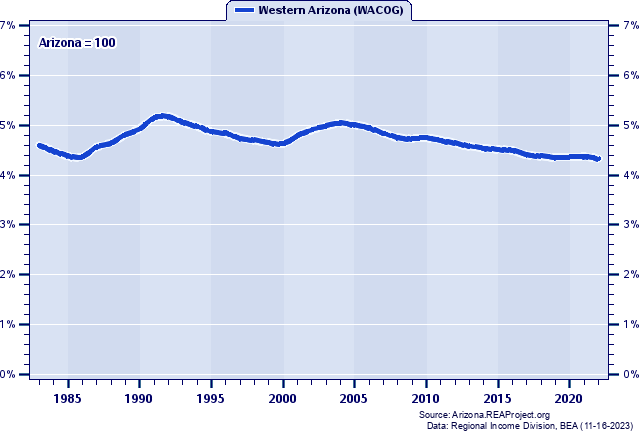 Figure 4. Another interesting and insightful way of contrasting the total employment growth of Western Arizona (WACOG) is to compare its individual percentage contributions to Arizona's statewide total employment over time, as shown in Figure 4. A rising share means a region's total employment grew faster, or declined less, than Arizona's total employment, while a declining share shows it grew more slowly. In 1983, Western Arizona (WACOG)'s total employment totaled 4.59% of Arizona's total employment, while in 2022 it totaled 4.33% thereby yielding a -0.26% share-shift.
Western Arizona (WACOG) Total Employment: Annual Percent Change, 1984-2022 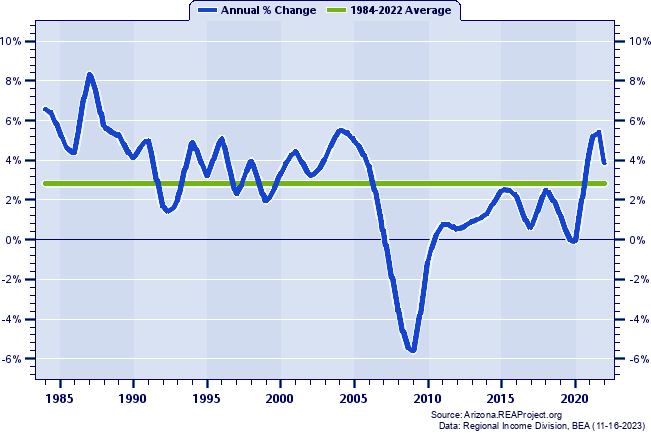 Figure 5. Figure 5 shows the short-run pattern of Western Arizona (WACOG)'s total employment growth by tracking the year-to-year percent change over 1984-2022. The average annual percent change for the entire 39-year period is also illustrated on this chart to provide a benchmark for gauging periods of relative high--and relative low--growth against the backdrop of the long-term average. On average, Western Arizona (WACOG)'s total employment grew at an annual rate of 2.83% over 1984-2022. Western Arizona (WACOG) posted its highest growth in 1987 (8.33%) and posted its lowest growth in 2009 (-5.59%). In 2022, Western Arizona (WACOG)'s total employment grew by 3.87% Western Arizona (WACOG) Total Employment: Annual Percent Change and Decade Averages Over 1984-2022 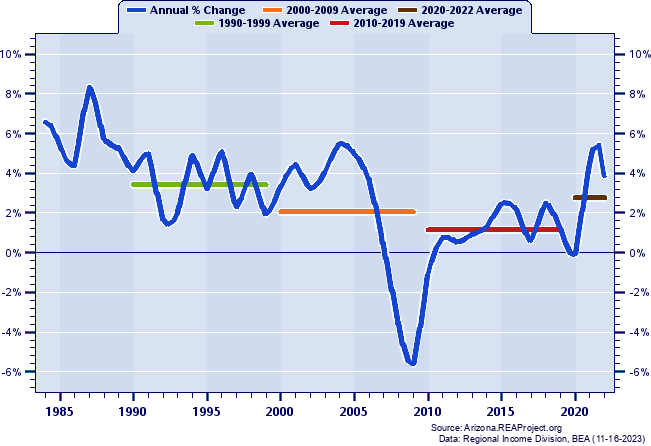 Figure 6. Over the past five decades some council of governments regions have experienced extreme swings in growth, and often such swings have tended to coincide with the decades themselves. Figure 6 again shows the annual percent change in Western Arizona (WACOG)'s total employment since 1984, but this time they are overlayed with average growth rates for the decade of the 1990s, 2000s, 2010s, and 2020-2022. During the 1990s, Western Arizona (WACOG)'s annual total employment growth rate averaged 3.43%. It averaged 2.05% throughout the 2000s, 1.15% in the 2010s, 2.77% thus far this decade (2020-2022). Total Employment Growth: Average Annual Percent Change by Decade 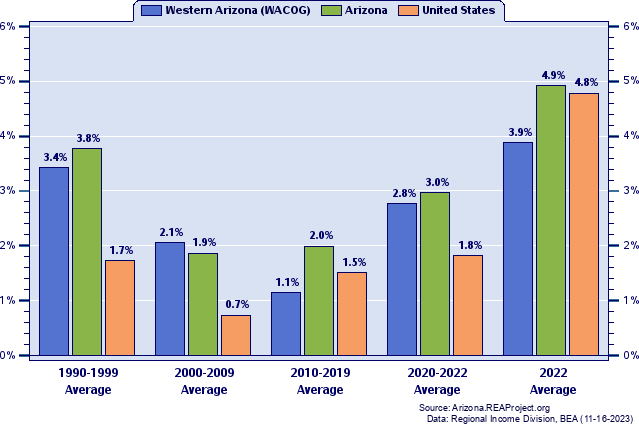 Figure 7. Figure 7 compares the decade average growth rates for Western Arizona (WACOG) noted in the previous graph with the corresponding decade averages for Arizona and the nation. As the chart reveals, Western Arizona (WACOG)'s average annual total employment growth amounted to less than Arizona's average throughout the 1990s (3.43% vs. 3.77%), registered above Arizona's average in the 2000s (2.05% vs. 1.87%), recorded under Arizona's average in the 2010s (1.15% vs. 1.99%), and fell below Arizona's average over the 3 year period of the current decade, 2020-2022 (2.77% vs. 2.97%). Finally, relative to nationwide total employment growth trends, Western Arizona (WACOG) recorded above the nation over the 1990s (3.43% vs. 1.73%), surpassed the nation over the 2000s (2.05% vs. 0.74%), fell below the nation over the 2010s (1.15% vs. 1.51%), and outpaced the nation over 2020-2022 (2.77% vs. 1.82%). Job Ratios (Employment/Population): 1983-2022 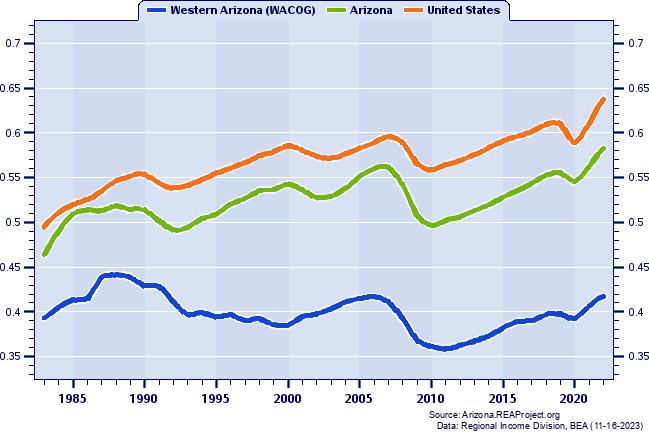 Figure 8. The job ratios shown in Figure 8 for Western Arizona (WACOG), Arizona and the nation not only portray a number of important trends, they also serves as a thumbnail guide to evaluating an economy's capacity to generate enough jobs fast enough to absorb the increasing number of workers attendant to a growing population. The job ratio is the number of full-time and part-time jobs by place of work, divided by population. Nationally, the job ratio rose from 0.49 to 0.64 between 1983 and 2022. Western Arizona (WACOG)'s job ratio registered 0.39 in 1983, and 0.42 in 2022. Underlying the rising job ratio over the past several decades have been the increases in the labor force participation rates, with the number and proportion of women in the labor market playing a leading role. An assortment of other factors can contribute to regional differences in the job ratio. They include differences in the proportion of elderly and retirees who no longer work and participate in the labor force, differences in the number and proportion of part-time vs. full-time workers, differences in industry composition, and differences in age and sex distribution and degree of urbanization. Also, a disproportionate number of workers commuting to work outside a county tends to lower its local county job ratio, while a net inflow of workers commuting to work inside the county tends to augment its local county job ratio. Avoid interpreting the job ratio as the fraction (or percent) of the local population employed. This interpretation should only apply to the "employment-population ratio" statistic compiled by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) from the Current Population Survey (CPS). Job Ratios (Employment/Population) as a Percent of the U.S. Average: 1983-2022 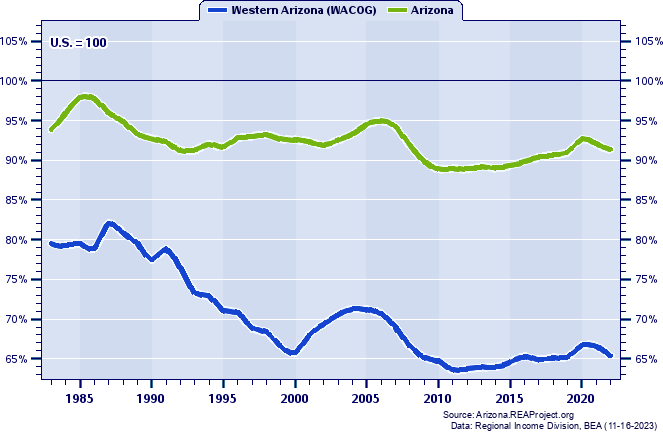 Figure 9. To highlight trends in a local job ratio relative to nationwide trends, Figure 9 tracks Western Arizona (WACOG)'s, Arizona's job ratio as a percent of the national job ratio over 1983-2022.
| Analysis Options Menu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||